The National Assembly of the Republic of Korea is the unicameral national legislature of South Korea that represents the people’s opinions. All the laws of the country are made by the National Assembly. At present, the members serve fouryear terms. The first National Assembly was launched on May 31, 1948. The 21st National Assembly was formed through the legislative elections on April 15, 2020.
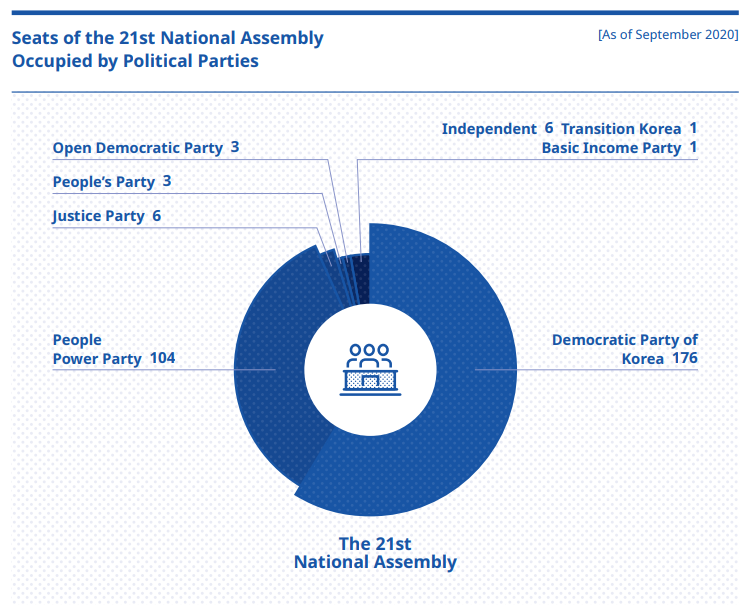
The National Assembly Proceeding Hall is located in Yeouido near the Hangang River that flows through Seoul. The National Assembly is composed of 253 members elected in local constituencies and 47 members elected through proportional representation. The latter are meant as a means of bringing persons with specific professional expertise into the assembly. As of September 2020, the ruling party is the Democratic Party of Korea, due to its plurality in the legislature. The leading opposition party is the People Power Party.
The executive power is vested in the Executive Branch headed by the President. Under the Constitution, the President shall be elected by universal, equal, direct and secret ballot by the people. The term of office of the President shall be five years, and the President shall not be reelected. President Yoon Suk Yeol took office on May 10, 2022, after winning the presidential election on March 9.
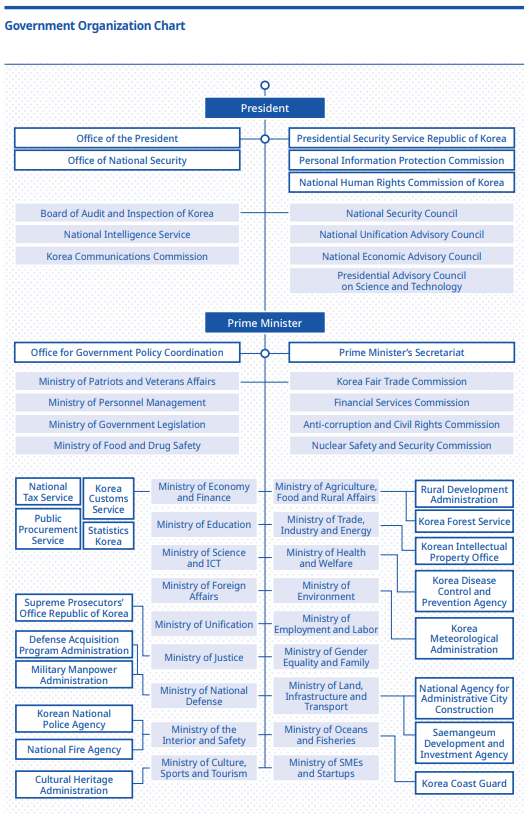
The State Council, usually referred to as the "Cabinet meeting" shall deliberate on important policies that fall within the power of the Executive. The President shall be the Chairperson of the State Council, and the Prime Minister shall be the Vice-Chairperson. If the office of the presidency is vacant or the President is unable to perform his or her duties for any reason, the Prime Minister controls the ministries of the government on his/her behalf. As of August 2020, the Executive Branch of the government operates 23 ministries, 18 administrative authorities, 2 boards, 4 offices, and 7 committees.
The Judiciary of the government is composed of the Supreme Court, appellate courts, district courts, family courts, administrative courts, and the patent court among others. The Supreme Court Chief Justice is appointed by the President with the consent of the National Assembly, and other Supreme Court justices are appointed by the President upon the recommendation of the Chief Justice. The term for the Chief Justice and justices is six years.



The National Assembly Proceeding Hall is located in Yeouido near the Hangang River that flows through Seoul. The National Assembly is composed of 253 members elected in local constituencies and 47 members elected through proportional representation. The latter are meant as a means of bringing persons with specific professional expertise into the assembly. As of September 2020, the ruling party is the Democratic Party of Korea, due to its plurality in the legislature. The leading opposition party is the People Power Party.
The executive power is vested in the Executive Branch headed by the President. Under the Constitution, the President shall be elected by universal, equal, direct and secret ballot by the people. The term of office of the President shall be five years, and the President shall not be reelected. President Yoon Suk Yeol took office on May 10, 2022, after winning the presidential election on March 9.
The State Council, usually referred to as the "Cabinet meeting" shall deliberate on important policies that fall within the power of the Executive. The President shall be the Chairperson of the State Council, and the Prime Minister shall be the Vice-Chairperson. If the office of the presidency is vacant or the President is unable to perform his or her duties for any reason, the Prime Minister controls the ministries of the government on his/her behalf. As of August 2020, the Executive Branch of the government operates 23 ministries, 18 administrative authorities, 2 boards, 4 offices, and 7 committees.
The Judiciary of the government is composed of the Supreme Court, appellate courts, district courts, family courts, administrative courts, and the patent court among others. The Supreme Court Chief Justice is appointed by the President with the consent of the National Assembly, and other Supreme Court justices are appointed by the President upon the recommendation of the Chief Justice. The term for the Chief Justice and justices is six years.

